The NH4+ ion is a spectator ion in this reaction, so it will not appear in the net ionic equation.
Fe3+ (aq) + 3 NH4+ (aq) + 3 OH�?/SUP> (aq) ––�?gt; Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3 NH4+ (aq)
"Cancelling" the 3 NH4+ ions on each side gives
Fe3+ (aq) + 3 OH�?/SUP> (aq) ––�?gt; Fe(OH)3 (s)
for the net ionic equation.
Steve
P.S. A solution of "ammonium hydroxide" actually contains very little NH4OH. It is mostly ammonia dissolved in water. Ammonia is a weak base that undergoes this reaction with water (called a weak base hydrolysis reaction):
NH3 (aq) + H2O (l) 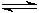 NH4+ (aq) + OH�?/SUP> (aq)
NH4+ (aq) + OH�?/SUP> (aq)
This is where ammonium hydroxide comes from. Ammonium hydroxide is not a stable compound (it decomposes back to NH3 and H2O) but solutions of ammonia in water are nevertheless often labeled "ammonium hydroxide."
 Free Forum Hosting
Free Forum Hosting