|  


What Is Reflexology
The Reflexology Association of Canada defines it as "A natural healing art, based on the principle that there are reflexes in the feet and hands which correspond to every part of the body." By stimulating and applying pressure to the feet or hands, you are increasing circulation and promoting specific bodily and muscular functions. Kevin Kunz, one of the pioneers of reflexology, puts it best -- "Imagine stepping on a tack. Your whole body reacts because of something perceived by the foot. Reflexology with a full range of pressure sensors, utilizes the same body system of fight or flight to relax the body." Indeed,
the feet and hands are more sensitive than most people realize. Similar to how we use our eyes to detect light, the hands and feet detect pressure, stretch, movement and weight distribution. 
The 1996 China Reflexology Symposium Report has found foot reflexology to be 93.63% effective in treating 63 disorders. After an analysis of 8,096 clinical cases, Dr. Wang Liang reported that reflexology was significantly effective (the cure) in 48.68% of all the cases, and an effective/improved treatment in 44.95% of the cases. Another study, in Britain, had fifteen women receive half-hour reflexology sessions for eight weeks. The findings included noticable physical and emotional improvements, increased self-esteem and confidence, an ability to stay motivated and be heard and taken seriously, and an improvement in concentration. 
Here are some important reminders before using reflexology.
Avoid use for one hour after meals.
Within 30 minutes after massage, you should drink at least 500 cc (cubic centimeters) of warm water; in cases of kidney or heart disease, you should drink no more than 150 cc of water.
Do not apply heavy pressure to bones.
In case of serious heart conditions, diabetes, or kidney problems, use at any time should be restricted to under 10 minutes.
In case of epilepsy, heart conditions, or high blood pressure, a physician should be consulted.
If after use of the massage board for a period of time, do not feel alarmed if an ailment seems to worsen or the mouth feels dry. This is normal, especially in the case of inflammation or rheumatism and will pass shortly. 
Although this natural healing technique has only recently gained recognition in the United States, it has actually been around for centuries. There is recorded evidence that the ancient Egyptians and Chinese practiced a form of reflexology before 2,330 B.C. The North American pioneer of Reflexology was Dr. William Fitzgerald, M.D., an ear-nose-throat specialist in Conneticut. In 1913, he became interested in zone therapy, the practice of alleviating pressure on specific parts of the body. Since then American doctors have explored the use of reflexology as a complimentary therapy in the treatment of their patients. In the early 1930's therapy assistant Eunice Ingham designated that because the human foot has a high degree of sensitivity, this area should receive therapeutic massage treatment. Today, reflexology is gaining acceptance by a growing number of therapists and medical professionals who are seeking complimentary forms of therapy for their patients.

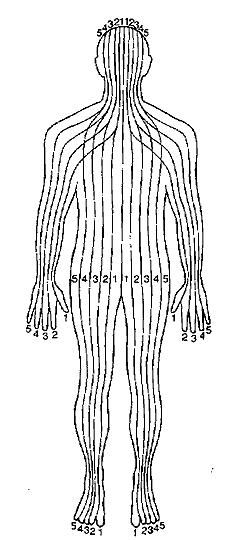
Reflexology is an ancient form of holistic treatment, with links to Egyptian, Chinese, Japanese and Indian cultures. It involves stimulating the nerve connections in the soles of the foot to balance and restore energy to various organs in the body. 
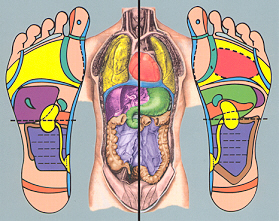
Reflexology is the science that deals with the principle there are areas on the feet and hands which correspond to the major glands and organs of the body. By using specific pressure on an area of the foot, an effect will be felt on the corresponding area of the body. Reflexology reduces stress and induces relaxation 
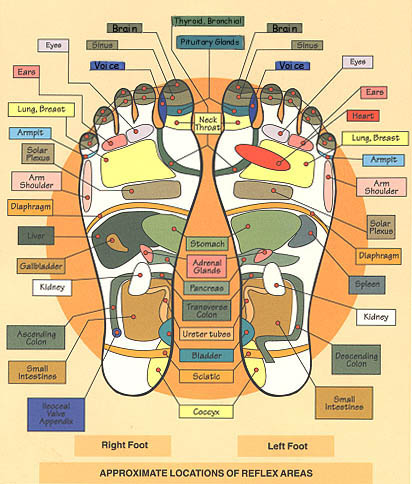
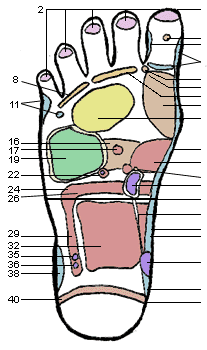
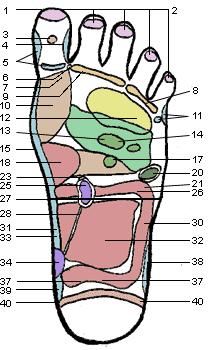
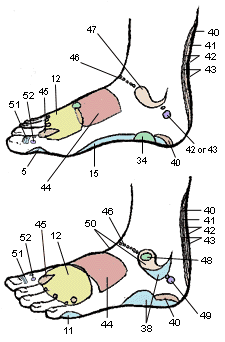
1. Top of Head
2. Sinuses
3. Pituitary Gland
4. Temporal Area
5. Neck, Cervical
6. Upper Lymph Area
7. Parathyroid Gland
8. Ears
9. Eyes
10. Thyroid Glands
11. Shoulder
12. Lungs and Bronchi
13. Heart Area
14. Heart
15. Spine, Vertebra
16. Pancreas
17. Solar Plexus
18. Stomach & Duodenum
19. Liver
20. Spleen
21. Spleenic Fixture
22. Gall Bladder
23. Adrenal Glands
24. Hepatic Flexure
25. Kidneys
26. Transverse Colon
27. Waist
28. Ureters
29. Ascending Colon
30. Descending Colon
31. Lumbar
32. Small Intestines
33. Sacral
34. Bladder
35. Ileo-Caecal Valve
36. Appendix
37. Sigmoid Flexure
38. Hip & Lower Back
39. Coccyx
40. Sciatic Area
41. Rectum
42. Uterus
43. Prostate
44. Breast
45. Lymph Drainage
46. Fallopian Tubes
47. Lymph Nodes (Arm Pit)
48. Sacro Iliac Joint
49. Ovary or Testicle
50. Lymph Nodes (Groin)
51. Maxilla/Submaxilla (Jaw)
52. Tonsils

Web Page and Backgrounds By Topaz/Sandy© This page is not shareware or linkware
And is designed exclusively for
A Jewel In The Crown Please do not copy or remove any part |
 Free Forum Hosting
Free Forum Hosting